Fiberglass Duct Rodder: Design Principles
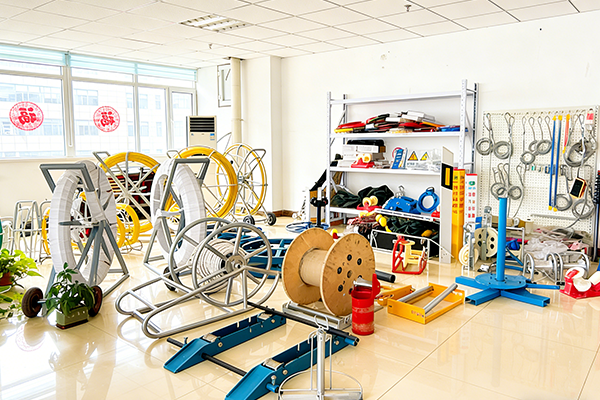
A fiberglass duct rodder is a specialized tool used for installing cables through conduits, ducts, and pipes in electrical, telecommunications, and utility applications. Its primary function is to facilitate the pulling of cables through long, often tortuous pathways with minimal friction and maximum control. Proper design ensures durability, flexibility, and user safety.
1. Material Selection
Fiberglass rods are preferred due to their combination of flexibility, strength, and lightweight properties:
High tensile strength allows the rod to push or pull cables without permanent deformation.
Flexural flexibility enables navigation through curved or angled ducts without kinking.
Lightweight construction reduces operator fatigue during extended use.
Fiberglass rods often include polyester or epoxy resin coatings to enhance surface smoothness and abrasion resistance.
2. Diameter and Length Considerations
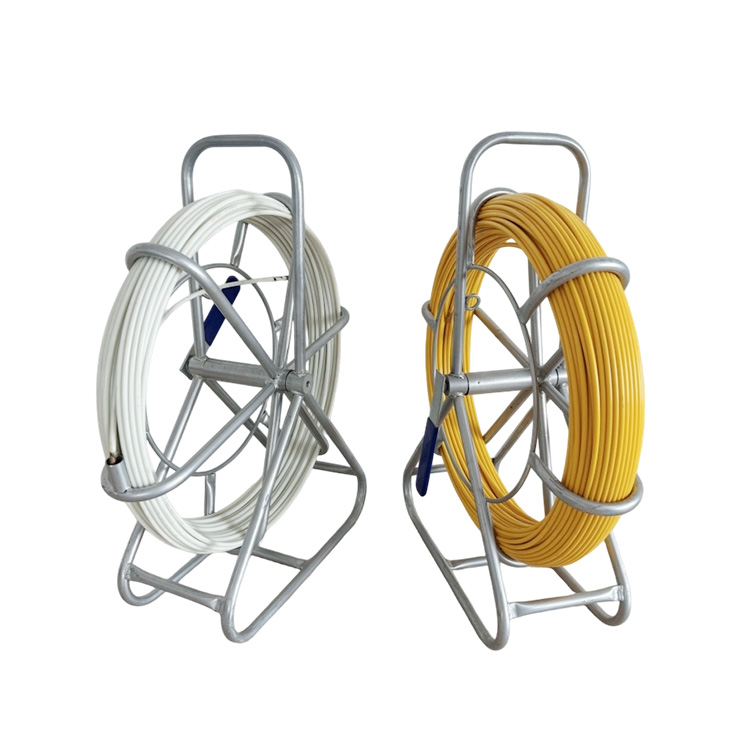
Rod diameter varies typically from 6 mm to 16 mm depending on duct size and cable load.
Longer rods are designed in modular sections to allow easy assembly and storage while accommodating various conduit lengths.
The rod stiffness must balance pushability with bendability, ensuring the rod can travel long distances without buckling.
3. Surface and Coating Design
Smooth, low-friction coatings reduce resistance during insertion, facilitating longer pulls and minimizing cable damage.
Anti-static coatings may be applied to prevent dust and debris accumulation.
End fittings are often metallic or high-strength plastic tips to withstand wear and allow attachment of pulling grips or hooks.
4. Handle and Ergonomics
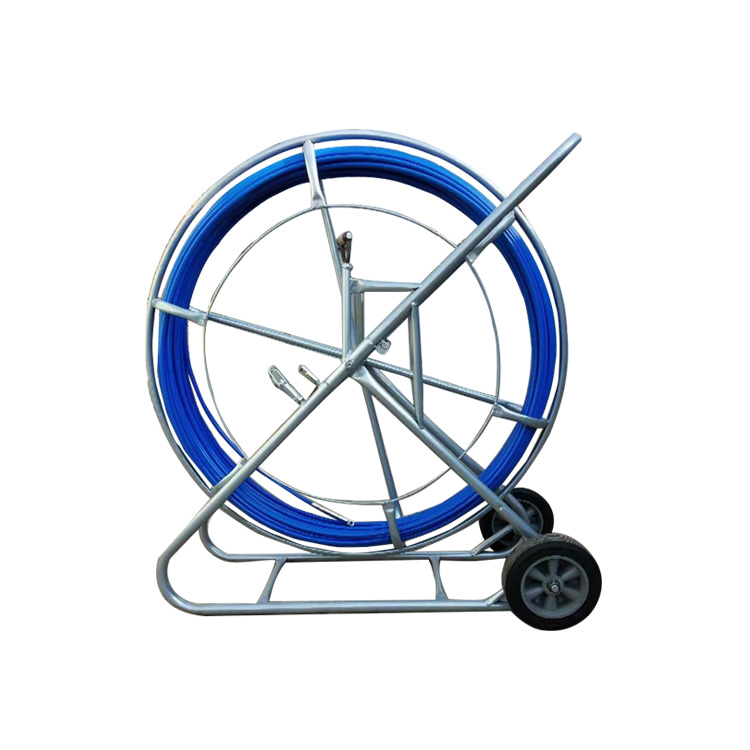
Handles should provide a comfortable grip and reduce operator strain.
Rotatable handles or reels may be incorporated to allow the rod to spin freely, reducing torsional stress on both the rod and the cable.
Ergonomic design minimizes the risk of repetitive strain injuries during repetitive pushing or pulling operations.
5. Modularity and Accessories
Rods are designed in interlocking segments to achieve the required length without compromising structural integrity.
End connectors allow attachment of pulling grips, fish tape, or cable sockets.
Optional reel systems store and deploy rods efficiently, improving safety and ease of handling.
6. Safety Considerations
Non-conductive fiberglass reduces the risk of electrical shock when working near energized circuits.
Rounded or blunted rod tips prevent conduit damage and reduce the risk of cable insulation damage.
Visibility markings or color coding may be included for easy identification in low-light environments.
Conclusion
The design of a fiberglass duct rodder must integrate material strength, flexibility, ergonomic handling, surface friction reduction, and modularity. By optimizing these parameters, manufacturers can provide a tool that enhances installation efficiency, reduces operator fatigue, and ensures safe, reliable cable deployment across various ducting systems.
References
Bartley, J. & Fisher, R. Utility Installation Tools Handbook. McGraw-Hill, 2018.
ASTM F2563 – Standard Specification for Fiberglass Rods for Cable Installation.
Gibson, R. (2020). “Design and Performance of Fiberglass Rods in Conduit Applications.” Journal of Electrical Installation Technology.
Strong, A. B. Plastics and Composites in Industrial Applications. Pearson, 2017.