Application Guide of Fiberglass Duct Rodder in Underground Pipeline Installation
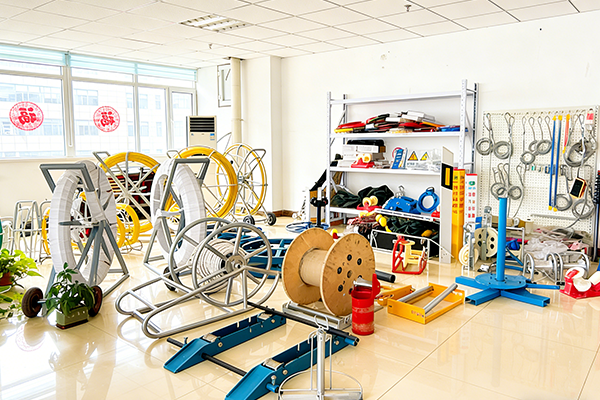
A fiberglass duct rodder is a widely used tool in underground pipeline installation, especially for pulling cables, ropes, or guide lines through conduits and ducts. Its high strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties make it an essential solution for municipal works, telecommunications, power utilities, and industrial pipeline projects.
1. What Is a Fiberglass Duct Rodder
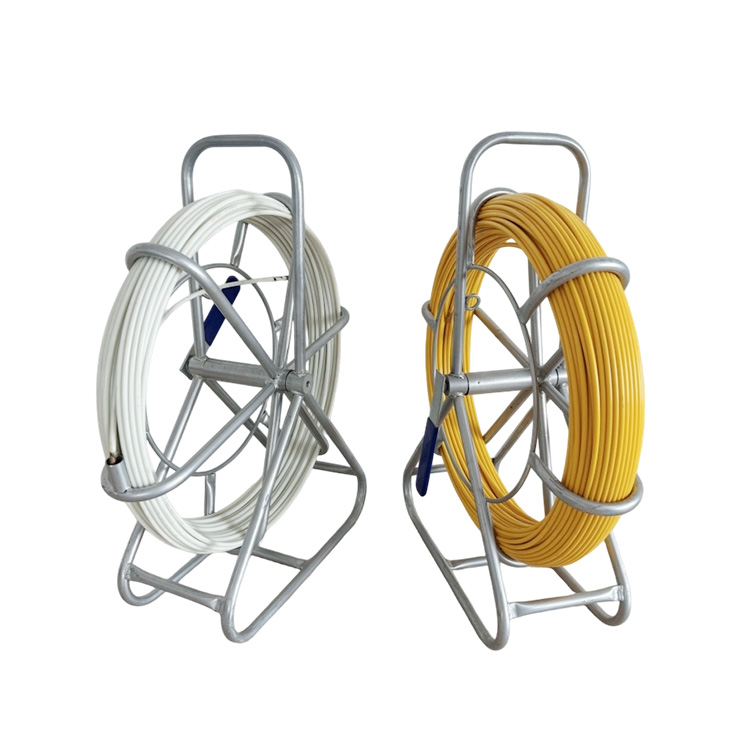
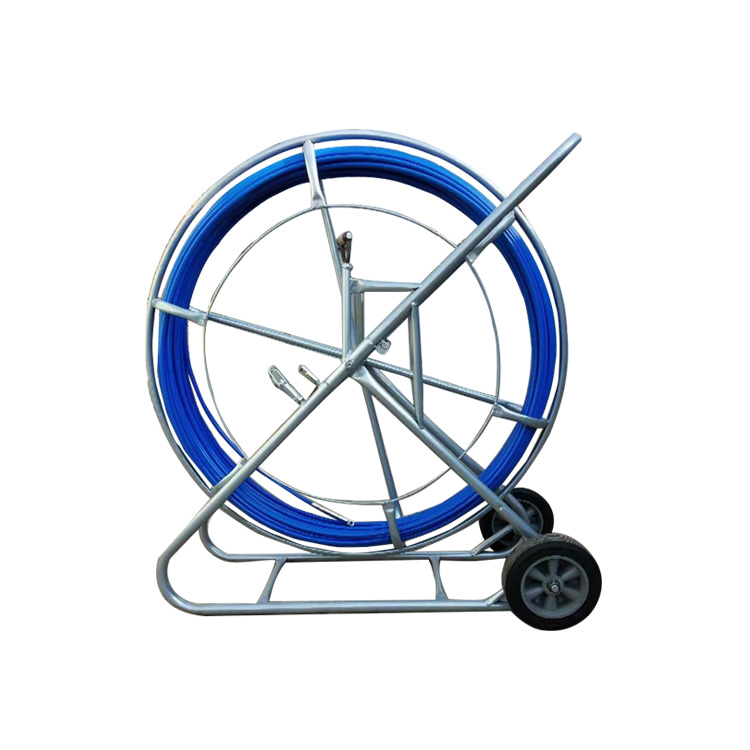
A fiberglass duct rodder is typically composed of a fiberglass-reinforced core with a protective outer coating, mounted on a frame or reel. It is designed to be pushed through underground ducts, conduits, or pipelines to establish a pull path for cables or other installations. Compared with steel rods, fiberglass rodders are lighter, safer near live electrical systems, and resistant to corrosion in wet or chemically aggressive environments.
2. Key Applications in Underground Pipeline Installation
Cable Routing and Pulling
Fiberglass duct rodders are commonly used to guide power cables, fiber optic cables, and communication lines through underground conduits. The rodder first passes through the duct, and the cable is then attached and pulled back smoothly.
Pre-Installation Duct Checking
Before cable installation, duct rodders help verify whether pipelines are blocked, collapsed, or misaligned. This reduces installation risks and prevents damage to expensive cables.
Municipal and Utility Projects
In urban underground infrastructure projects, duct rodders are used for sewer monitoring cable placement, traffic signal wiring, and street lighting systems where direct trenching is limited.
Pipeline Maintenance and Retrofit
During renovation or expansion of existing underground systems, fiberglass duct rodders enable new cable installation without disturbing existing structures or road surfaces.
3. Advantages of Fiberglass Duct Rodders
High Strength with Flexibility
Fiberglass provides an excellent balance between stiffness and flexibility, allowing the rodder to navigate bends and long-distance ducts while maintaining pushing force.
Electrical Insulation
Unlike metal tools, fiberglass duct rodders are non-conductive, significantly improving safety when working near live electrical cables.
Corrosion and Moisture Resistance
Fiberglass is resistant to rust, moisture, and many chemicals, making it suitable for underground and harsh environments.
Lightweight and Portable
Compared to steel alternatives, fiberglass rodders are easier to transport and operate, improving efficiency on job sites.
4. Best Practices for Use
Operators should select the appropriate rod diameter and length based on duct size and distance. During use, steady and controlled pushing reduces the risk of rod breakage. Protective gloves are recommended to improve grip and reduce wear on the rod surface. After use, cleaning and proper storage help extend service life.
5. Safety Considerations
Although fiberglass is electrically insulated, users should still follow standard safety procedures when working near live systems. Avoid excessive bending beyond the minimum radius specified by the manufacturer, as this may weaken the rod over time.
6. Conclusion
Fiberglass duct rodders play a vital role in modern underground pipeline installation by improving efficiency, safety, and installation accuracy. Their durability, insulation properties, and adaptability make them an indispensable tool for utility contractors and infrastructure professionals.
References
ASTM D7097 – Standard Guide for Application of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Products in Infrastructure.
IEEE 979 – Guide for Subsurface Installation of Electrical Cables.
CEN EN 61386 – Conduit Systems for Cable Management.
Harper, C. A. Handbook of Fiber Reinforced Plastics. McGraw-Hill, 2002.
OSHA Technical Manual – Underground Construction and Utility Safety Guidelines.