Proper Use of a Cable Puller to Avoid Cable Damage
Cable pullers are essential tools for installing electrical, telecommunications, and power cables through conduits, ducts, or trenches. Improper use can lead to cable insulation damage, conductor breakage, or reduced service life. Following proper handling and operational guidelines ensures safe, efficient installation while protecting cable integrity.
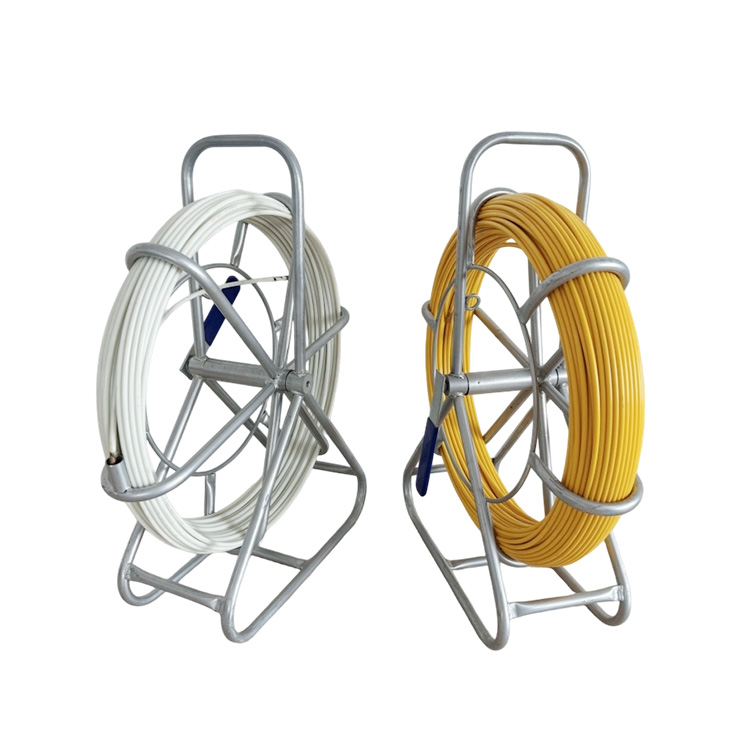
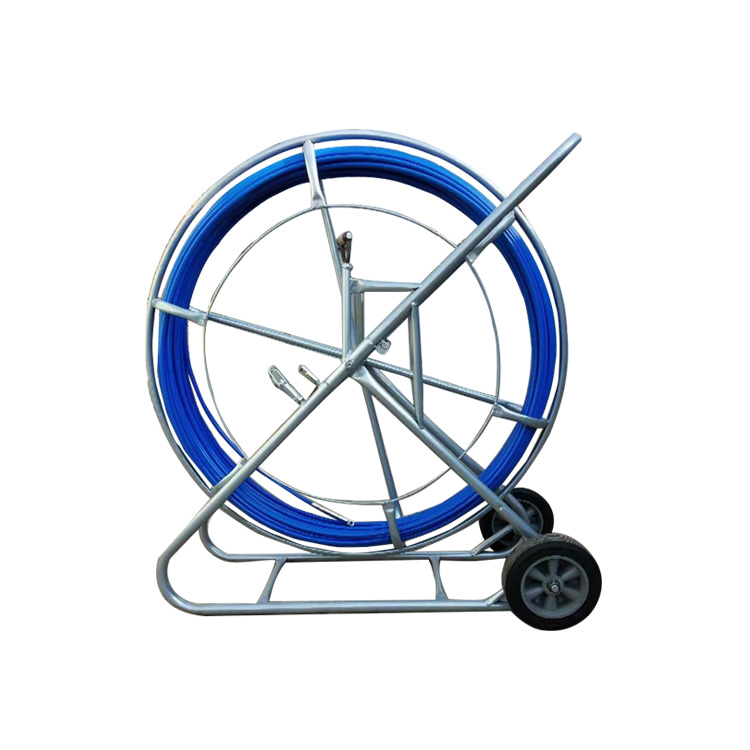
1. Select the Appropriate Cable Puller
Capacity: Choose a cable puller rated for the cable size and weight. Overloading can deform or stretch the cable.
Type: Use mechanical, hydraulic, or manual pullers based on conduit length, cable diameter, and installation environment.
Attachments: Ensure pulling grips, rollers, or clamps are compatible with the cable type to avoid crushing or abrasion.
2. Inspect Cables and Equipment Before Use
Check the cable for cuts, nicks, or insulation defects before pulling.
Inspect the puller, grips, rollers, and sheaves for wear or sharp edges that could damage the cable.
Ensure that the conduit or duct is clear of obstructions or debris.
3. Maintain Proper Tension and Pulling Speed
Avoid excessive pulling force that can stretch or damage the cable.
Monitor the cable’s tension continuously; use a dynamometer if necessary for long runs.
Pull at a steady, moderate speed to reduce friction and prevent kinking.
4. Reduce Friction During Installation
Use cable lubricant compatible with the cable type to ease pulling through conduits or tight bends.
Employ rollers or sheaves at corners or entry points to minimize abrasion and bending stress.
Avoid sharp bends; follow the cable manufacturer’s minimum bend radius guidelines.
5. Proper Handling of Cable Ends
Secure cable ends with proper grips or pulling eyes to distribute force evenly.
Protect exposed conductors with tape or caps to prevent snagging or insulation damage.
Ensure the pulling path is free of obstacles that could catch or crush the cable.
6. Post-Installation Checks
Inspect the cable after pulling for any scratches, abrasions, or deformation.
Verify conductor continuity and insulation integrity with electrical testing if necessary.
Reposition or replace damaged sections before energizing the cable system.
Conclusion
Correct use of a cable puller involves selecting the right equipment, inspecting both cable and tools, controlling pulling tension and speed, reducing friction, and following manufacturer guidelines for bend radius and handling. These practices minimize the risk of cable damage and ensure safe, efficient installation in conduit or duct systems.
References
National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA). NECA Wiring Methods Manual, 2020.
Bartley, J., & Fisher, R. Utility Installation Tools Handbook. McGraw-Hill, 2018.
IEC 60364-5-52 – Selection and Erection of Electrical Equipment – Wiring Systems.
Gibson, R. (2021). “Safe Cable Pulling Techniques to Prevent Conductor Damage.” Journal of Electrical Installation Technology.